Focus on EcoScope Models: The Israeli EEZ ecosystem model
Author: Eyal Ofir, IOLR
Within the context of the EU-funded EcoScope initiative, the team at the Israel Oceanographic and Limnological Research (IOLR) developed an Ecopath model (EwE), specifically tailored for the Israeli Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ). This Ecopath model stands as a fundamental building block for subsequent Ecosim and Ecospace models. Its construction was driven by the imperative of aligning it with the unique characteristics of the Israeli marine ecosystem.

Map of he Israeli EEZ ecosystem model
The adaptation of the Ecopath model hinged upon three overarching objectives that sought to harmonise it with the required Ecospace model. These pivotal objectives included:
- Addressing the Invasive species challenge: The first objective centred on comprehensively understanding the impact of invasive species on the local ecosystem. A primary concern was evaluating the potential displacement of native species from their natural habitats due to invasive species encroachment.
- Exploring Deep-Sea Dynamics: The second objective aimed at unravelling the mysteries of the deep-sea ecosystem within the Israeli EEZ. Focusing on the distribution patterns and behaviours of deep-sea species, this objective was important to allow the incorporation of our understanding of the deep-sea habitat.
- Examining Fishing Policy Implications: The third objective focused on the fishing policies and their effects on the ecosystem. By simulating various fishing scenarios and policy changes, in tandem with future climate change, the modified Ecopath model sought to predict the ecological outcomes of shifts in fishing practices, vital for sustainable fisheries management.
To accomplish these objectives effectively, a new Ecopath model was developed. The model structure included the categorisation of species into distinct groups, differentiating between fish and invertebrates, and further classifying them based on their habitats, continental shelf, slope, and deep sea. Additionally, a clear separation between invasive and native species was introduced to address the unique challenges posed by invasive organisms. Updating the species list with data from the IOLR database ensured the model’s accuracy and relevance.
The Israeli continental shelf area faces a multitude of environmental pressures. These pressures encompass natural phenomena like climate change and rising seawater temperature, as well as the introduction of Red Sea species, which is altering the ecological balance. Human activities, notably fishing, also contribute to the complex dynamics of the ecosystem.
The development of the Ecopath model not only facilitates an examination of required fishing policies within the Israeli EEZ but also accommodates the consideration of additional processes specific to the region. This multifaceted approach allows for a comprehensive assessment of policy needs in ecosystems exposed to a wide array of pressures.
Moreover, the model’s application within the Israeli EEZ presents an opportunity to explore broader ecological processes in the Eastern Mediterranean. This region serves as a crucial transit hub for invasive species routes to the central Mediterranean, underscoring the model’s regional significance.
Focus on regional EcoScope models
Within EcoScope, eight case-study areas are identified: The Bay of Biscay, The Aegean Sea, The North Sea, The Israeli EEZ, The Black Sea, The Balearic Islands, The Western Baltic Sea, and The Adriatic Sea.
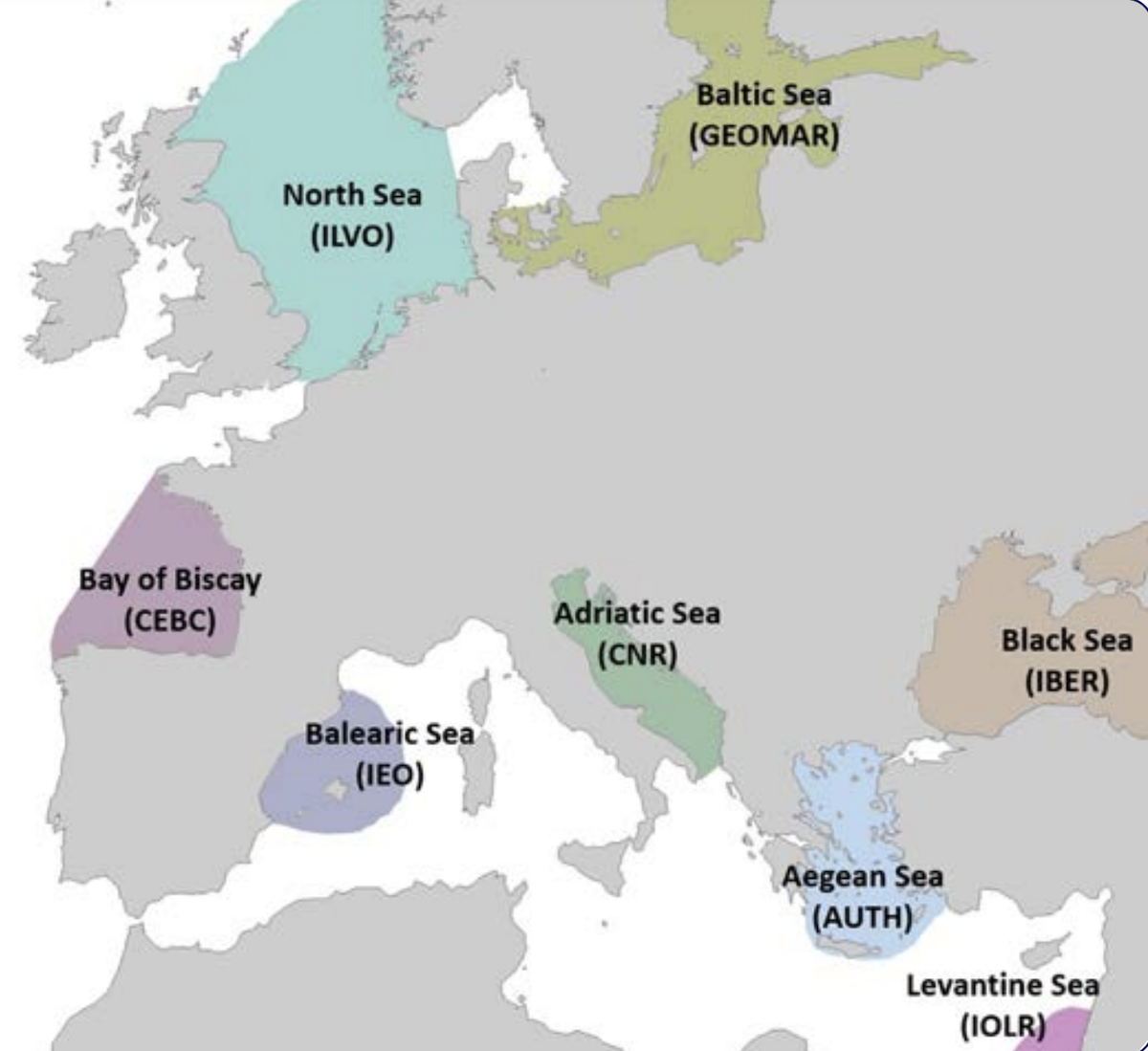
Map of the European and Levantine Seas highlighting 8 case studies regions investigated





